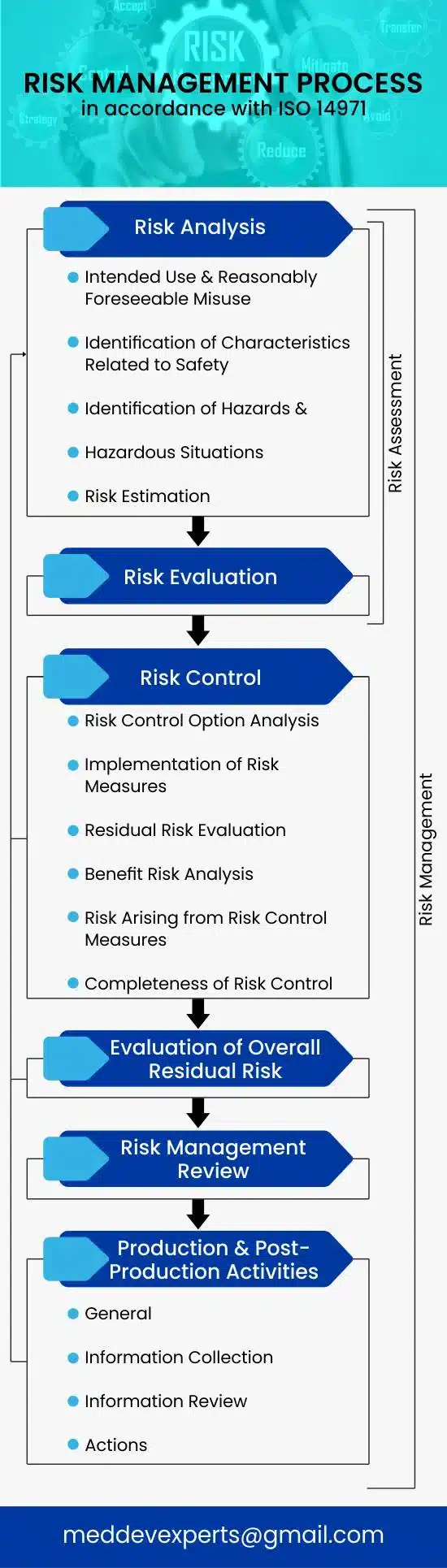
Risk Management of Medical Devices in Accordance with ISO 14971:2019
This article is to assist manufacturers of medical devices to identify the hazards associated with the medical device, including software as a medical device, and in vitro diagnostic medical devices to estimate and evaluate the associated risks, control these risks, and monitor the effectiveness of the controls throughout the life cycle of a medical device. Risk management is an integral part of a quality management system. This article outlines key requirements, such as risk management process, management responsibilities, personnel competence, risk management plan, and risk management file in accordance with ISO 14971:2019.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. General Requirements for Risk Management System
1.1 Risk Management Process
Manufacturer’s must continuously manage risks by identifying hazards, evaluating, controlling, and monitoring them throughout the medical device’s entire life cycle. This includes risk analysis, evaluation, control, production, and post-production. If there’s a product realization process, it should incorporate relevant risk management aspects.
1.2 Management Responsibilities
Top management must commit to the risk management process by allocating resources and appointing competent personnel. They must establish and document a policy for risk acceptability criteria, considering regulations, standards, and stakeholder concerns. Regular reviews ensure the process’s effectiveness, with decisions and actions documented, and can be integrated into the quality management system review, if applicable.
1.3 Competence of Personnel
Personnel in risk management must have the required education, training, skills, and experience. They should be knowledgeable about the specific medical device or similar devices, their use, technologies, and risk management techniques. Competence records must be kept up to date.
1.4 Risk management plan
A risk management plan must be documented in the risk management file. It must cover:
- Scope of risk management activities for the specific medical device and relevant life cycle phases.
- Assignment of responsibilities and authorities.
- Requirements for reviewing risk management activities.
- Criteria for risk acceptability based on the manufacturer’s policy, even when harm probability is uncertain.
- Method to assess overall residual risk and criteria for acceptability based on the manufacturer’s policy.
- Verification of risk control measures’ implementation and effectiveness.
- Activities for collecting and reviewing production and post-production data.
1.5 Risk Management File
The manufacturer must create and maintain a risk management file for the specific medical device. The file must trace each identified hazard to:
- Risk analysis
- Risk evaluation
- Implementation and verification of risk control measures
- Results of the evaluation of residual risks
The risk management file may include records from other required files. It should have references or pointers to the necessary information, enabling timely access by the manufacturer.
2 Risk analysis
2.1 Risk analysis process
The manufacturer must analyze risks for the medical device based on intended use and foreseeable misuse, identifying safety characteristics, hazards, and estimating risks. All analysis activities and outcomes should be documented in the risk management file.
2.2 Intended use and reasonably foreseeable misuse
The manufacturer must document the medical device’s intended use, including factors like medical indication, patient population, body part or tissue involved, user profile, use environment, and operating principle. They should also document reasonably foreseeable misuse.
2.3 Identification of characteristics related to safety
The manufacturer must identify and document qualitative and quantitative characteristics that could impact the safety of the specific medical device. If applicable, they should also define limits for these characteristics.
2.4 Identification of hazards and hazardous situations
The manufacturer must document known and foreseeable hazards related to the medical device, considering its intended use, foreseeable misuse, and safety characteristics. For each hazard, they should assess foreseeable events leading to hazardous situations and document them.
2.5 Risk estimation
For each hazardous situation, the manufacturer must estimate associated risks using available information. If harm probability cannot be estimated, consequences should be listed for risk evaluation. Results of estimations and categorizations must be recorded in the risk management file. The system for categorizing probability and severity of harm must be documented as well.
3 Risk Evaluation
During risk evaluation, the manufacturer must assess estimated risks for each hazardous situation and check if they meet the criteria in the risk management plan. If the risk is acceptable, further risk control activities are not required, and the estimated risk is treated as residual risk. However, if the risk is unacceptable, the manufacturer must proceed with risk control measures.
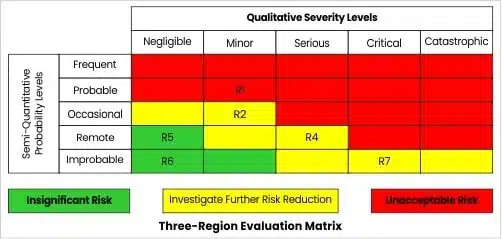
3.1 Example of a Three-Region Evaluation Matrix
Below is an example of a risk where the acceptable region of the matrix has been further subdivided. The estimated risks (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7,) have been entered into the appropriate cells.
4 Risk Control
4.1 Risk control option analysis
During risk control, the manufacturer must analyze and select appropriate measures to reduce risks to an acceptable level. The following risk control options should be used in the listed priority order:
a) Inherently safe design and manufacture.
b) Protective measures within the medical device or during manufacturing.
c) Providing safety information and, if needed, training to users.
4.2 Implementation of risk control measures
The manufacturer is responsible for implementing the risk control measures. After implementing each measure, they must conduct verification to ensure the effectiveness of the implemented risk control measure.
4.3 Residual risk evaluation
After implementing risk control measures, the manufacturer must evaluate the residual risk using defined criteria and document the results. If the residual risk is unacceptable, additional risk control measures should be considered until it becomes acceptable, as per the defined criteria. This process may continue until an acceptable residual risk level is achieved.
4.4 Benefit-risk analysis
If the residual risk remains unacceptable despite implementing additional risk control measures and it’s impractical to apply more measures, the manufacturer can conduct a benefit-risk analysis. They may gather and review data to assess if the benefits of using the medical device outweigh the identified risk. If the evidence doesn’t support this, the manufacturer can consider modifying the device or its intended use.
4.5 Risks arising from risk control measures
After implementing risk control measures, the manufacturer must conduct a review to assess the effects of these measures. The review should focus on whether:
a) New hazards or hazardous situations are introduced as a result of the risk control measures.
b) The estimated risks for previously identified hazardous situations are affected by the implementation of the risk control measures.
If any new hazards or hazardous situations are identified or if the estimated risks for previously identified hazardous situations are affected, the manufacturer must manage these risks according to the risk management process.
4.6 Completeness of risk control
The manufacturer must conduct a review of the risk control activities to ensure that:
a) All risks associated with identified hazardous situations have been considered.
b) All risk control measures for managing these risks have been implemented and completed.
The purpose of this review is to verify that the risk management process is comprehensive and all potential risks are adequately addressed.
5 Evaluation of overall residual risk
After implementing and verifying all risk control measures, the manufacturer must evaluate the overall residual risk of the medical device, considering remaining risks in relation to benefits. The criteria defined in the risk management plan should guide this evaluation. If the overall residual risk is acceptable, the manufacturer must inform users about significant remaining risks and provide necessary information for informed decision-making.
6 Risk management review
Before the medical device is commercially distributed, the manufacturer must conduct a risk management review. This review should ensure the following:
a) Proper implementation of the risk management plan.
b) Acceptability of the overall residual risk.
c) Availability of appropriate methods to collect and review information during the production and post-production phases.
The outcomes of this review, known as the risk management report, should be documented and included in the risk management file.
7 Production and post-production activities
7.1 General
The manufacturer must create, document, and maintain a system to actively collect and review information related to the medical device during its production and post-production phases.
When setting up this system, the manufacturer should consider suitable methods for effectively collecting, processing, and analyzing the information. This ensures that potential issues or risks can be identified and addressed promptly throughout the medical device’s life cycle.
7.2 Information collection
During the medical device’s life cycle, the manufacturer should collect relevant information from various sources, including:
a) Information generated during the production process and monitoring of production.
b) Information generated by users of the medical device.
c) Information generated by those responsible for installing, using, and maintaining the medical device.
d) Information generated by the supply chain involved in the production and distribution of the medical device.
e) Publicly available information that may pertain to the medical device or similar devices.
f) Information related to the generally acknowledged state of the art, which includes the latest advancements and knowledge in the field.
Collecting information from these sources helps the manufacturer to gather comprehensive data to assess the medical device’s performance, safety, and potential risks throughout its life cycle.
7.3 Information review
The manufacturer must review all collected information, focusing on safety relevance. This aims to identify:
• Unrecognized hazards or hazardous situations not initially identified during risk management.
• Hazardous situations with now unacceptable estimated risks.
• Cases where the overall residual risk is no longer acceptable relative to intended use benefits.
• Changes in the acknowledged state of the art that could impact device safety.
7.4 Actions
When relevant safety information is collected, the manufacturer must:
• Review the risk management file for reassessment of existing risks and/or assessment of new risks based on the new information.
• If a residual risk becomes unacceptable, evaluate the impact on implemented risk control measures and consider modifying the device.
• Assess the need for actions on already marketed devices affected by the new information.
• Record all decisions and actions in the risk management file.
• Evaluate the impact of new information on previous risk management activities.
• Use the evaluation results to review the risk management process’s suitability with top management.
8 Conclusion
In conclusion, implementing a robust risk management system in accordance with ISO 14971:2019 is crucial for medical device manufacturers to ensure the safety and effectiveness of their products throughout their entire life cycle. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, manufacturers can identify potential hazards, estimate associated risks, and implement appropriate control measures to mitigate those risks effectively.
Manufacturers must document all risk management activities in a comprehensive risk management file, which includes the analysis, evaluation, and control of risks, as well as the verification of implemented measures and assessment of residual risks.
Look no further! MedDev Experts, a trusted medical device consulting company, specializes in providing comprehensive services to develop your medical device risk management file in accordance with ISO 14971:2019.




Wow, incredible blog structure! you make blogging look easy. The whole glance of your site is
magnificent, as well as the content material!